Secure Your Smart Devices: An Essential SSH IoT Tutorial For Remote Control
Are you looking to take control of your smart devices, perhaps even managing them from afar? If you're curious about remote access for your IoT gadgets, then you've come to the right spot. Secure Shell, or SSH, is a truly vital tool when it comes to keeping devices safe within the vast Internet of Things (IoT) environment. Think of it, perhaps, like a very careful gatekeeper, making sure that only the right people get in while keeping out those who might cause trouble. With billions of IoT devices now linked up across the globe, knowing how to use SSH is almost like having a secret advantage for keeping things secure.
This article will walk you through setting up remote access to your IoT devices using SSH. We’ll cover how to get SSH ready on your device, how to set up the connection from your computer, and some good habits to keep your connections safe. This SSH remote IoT tutorial simplifies the whole process of getting SSH ready for IoT devices, making it quite accessible even for folks just starting out. You see, with more and more IoT devices showing up in homes, businesses, and even big industries, the need for secure ways to talk to them and manage them from a distance becomes really important.
So, if you’re here, chances are you’re looking for a way to remotely manage your smart devices without putting them at risk from cyber threats. This guide aims to show you the basics of creating a safe setup for your IoT devices using SSH. We will look into understanding IoT security concerns, getting a protective barrier ready, configuring SSH for secure entry, and putting in place good habits for ongoing safety. By following the suggestions and pointers provided, you can manage your IoT devices remotely with confidence, ensuring both safety and smooth operation in what you do, you know?
- Who Is The Highest Paid Qb In Nfl History
- Who Is Richer Peyton Manning Or Tom Brady
- Who Did Hayden Hopkins Have A Baby With
- Does Tom Brady Own A House In Florida
- How Much Does Hamlin Make Per Year
Table of Contents
- Why SSH is Your IoT's Best Friend
- Getting Started: Preparing Your IoT Device for SSH
- Connecting Securely: Your First SSH Session
- Beyond the Basics: Advanced SSH for IoT
- Keeping Your IoT SSH Connections Safe
- Troubleshooting Common SSH IoT Issues
- Frequently Asked Questions About SSH IoT Access
- Your Next Steps for Secure IoT Management
Why SSH is Your IoT's Best Friend
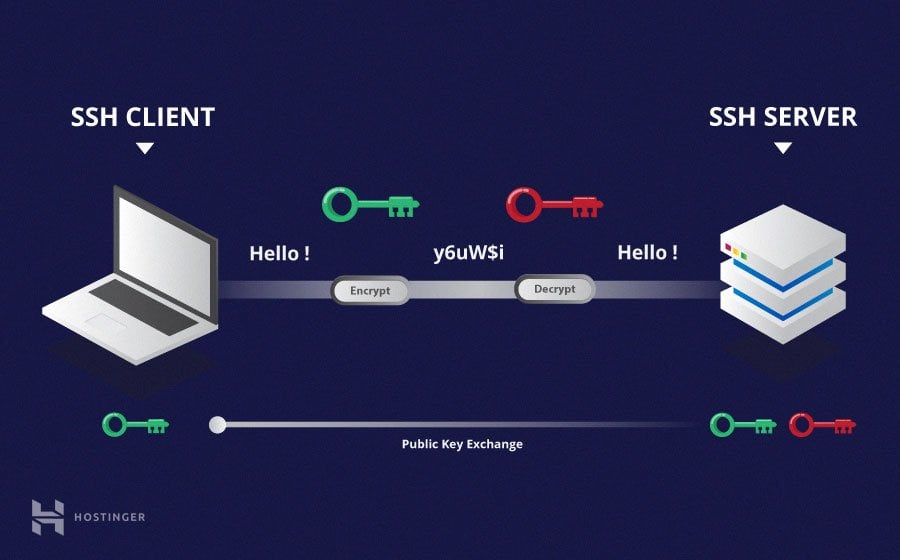
So, you might wonder why SSH is such a big deal for your small, connected devices. Well, it's quite simple, really. SSH provides a secure way to talk to your devices over an unsecured network, like the internet. This means that even if someone were to try and listen in on your connection, they wouldn't be able to make sense of the data, which is a very comforting thought.
For companies, allowing remote SSH access for IoT devices safely is a major plus. It means technicians can check on, fix, or update devices that are far away without needing to be there in person. This saves a lot of time and resources, obviously. It truly makes managing many devices much, much simpler.
Keeping Your Devices Safe
One of the main reasons to use SSH with your IoT devices is for the safety it brings. When you connect to a device using SSH, all the information exchanged is encrypted. This makes it incredibly difficult for anyone trying to snoop on your connection to see what you are doing or what data your device is sending. It's like putting your conversations in a coded language that only you and your device can understand, you know?
- What Nfl Team Is Moving To Las Vegas
- Where Is The Super Bowl 2025 Location
- How Much Does Martha Maccallum Make
- Who Is The 26 Year Old Nfl Owner Dating
- Which Nfl Team Is Not Owned By Anyone
This protective layer is especially important for IoT devices, which often handle sensitive information or control things in your home or business. Without proper security, these devices could become easy targets for cyber-attacks, leading to data breaches or even physical harm if they control machinery. So, using SSH is a fundamental step in protecting your little gadgets from potential trouble.
Accessing Devices from Anywhere
Another big benefit of SSH is the ability to manage your IoT devices from almost any location. Whether you're at home, at work, or on vacation, as long as you have an internet connection, you can connect to your devices. This is incredibly useful for troubleshooting, performing updates, or simply checking the status of your smart gadgets, which is pretty cool.
Imagine being able to control your IoT devices from a distance. If a sensor stops working in a remote area, you can log in, check the logs, and maybe even restart the service without having to drive out there. This kind of remote control brings a huge amount of convenience and efficiency to managing your connected world, very much so.
Getting Started: Preparing Your IoT Device for SSH
Before you can start connecting to your IoT devices using SSH, you need to make sure the device itself is ready. This involves a few steps, from choosing the right device to getting its operating system set up and then turning on the SSH feature. It's not too difficult, but it does require a bit of careful attention to detail, actually.
This SSH remote IoT tutorial will show you the simple steps to get going. We'll cover how to get SSH ready on your device, how to set up the connection from your computer, and some good habits to keep your connections safe. It's all about making sure your initial setup is solid, which is a good way to start.
Picking the Right Device
Not all IoT devices are built the same when it comes to SSH access. Generally, devices that run a full operating system like Linux, such as a Raspberry Pi, BeagleBone, or certain single-board computers, are the easiest to set up with SSH. These devices offer the flexibility needed to install and configure SSH servers. Some smaller microcontrollers might require more complex setups, perhaps involving a gateway device, which can be a bit more involved.
When you're choosing a device for your project, consider whether it has a network connection (Wi-Fi or Ethernet) and if it supports a Linux-based operating system. These features will make the SSH setup much smoother. For instance, a Raspberry Pi is a very popular choice for this kind of work because it's so versatile, you know?
Setting Up Your Device's Operating System
Once you have your chosen IoT device, the next step is to get its operating system ready. For many popular IoT boards, this means flashing an image of a Linux distribution onto an SD card or internal storage. Distributions like Raspbian (now Raspberry Pi OS) for Raspberry Pi are common choices because they are lightweight and come with many tools pre-installed, or are easy to add.
During this setup, you'll typically connect a keyboard, mouse, and monitor directly to the device for the first boot. You'll set up basic things like the time zone, keyboard layout, and perhaps create a user account. This initial hands-on setup is quite important for getting everything just right before you try to connect remotely, so it's worth taking your time.
Enabling SSH on Your Device
After your device's operating system is up and running, you'll need to enable the SSH server. The exact steps for this can vary a bit depending on your device and its operating system. For Raspberry Pi OS, for instance, you can often enable SSH through the `raspi-config` tool, which is a command-line utility for system configuration. You simply go into the "Interface Options" and enable SSH, which is pretty straightforward.
Alternatively, you can manually install the SSH server package, usually called `openssh-server`, using your system's package manager (like `apt` on Debian-based systems). After installation, the SSH service usually starts automatically, but you might need to check its status or enable it to start on boot. This step is, arguably, the most important part of getting your device ready for remote access.
Connecting Securely: Your First SSH Session
With your IoT device prepared, it's time to make your first secure connection. This is where the magic happens, as you finally get to talk to your device without being physically next to it. The process is quite similar regardless of whether you're using a Windows, macOS, or Linux computer, which is a nice bit of consistency.
This guide will walk you through setting up remote access to your IoT devices using SSH, ensuring your connections remain protected and efficient. It's a very satisfying moment when that first connection works, you know? It truly opens up a lot of possibilities for managing your devices.
From Your Computer: Windows, macOS, Linux
For macOS and Linux users, SSH is typically built right into the terminal application. You don't need to install anything extra, which is super convenient. Just open your terminal, and you're ready to go. Windows users, however, might need to take an extra step. Modern versions of Windows (Windows 10 and 11) now include an OpenSSH client by default, which is great. You can access it through PowerShell or Command Prompt. For older Windows versions, you might need to install a third-party client like PuTTY, which is a popular choice and quite reliable, too.
No matter your operating system, the concept remains the same: you'll be typing commands into a command-line interface to initiate the SSH connection. This consistency makes it easier to learn and apply across different systems. It's a bit like learning a universal language for talking to computers, in a way.
The Basic SSH Command
The fundamental command to connect to your IoT device via SSH is pretty straightforward. It usually looks something like this: `ssh username@device_ip_address`. The `username` is the account you want to log in as on your IoT device (often 'pi' for Raspberry Pi devices), and `device_ip_address` is the network address of your IoT device. You'll need to find your device's IP address on your local network, which can usually be done through your router's administration page or by running a command on the device itself, such as `hostname -I`.
For example, if your Raspberry Pi's username is 'pi' and its IP address is `192.168.1.100`, you would type `ssh pi@192.168.1.100` into your terminal. The first time you connect, you might see a message about the host's authenticity not being established; you'll typically type 'yes' to continue. This adds the device's unique identifier to your computer's list of known hosts, which is a good security measure.
Handling Passwords and Keys
After you enter the SSH command, you'll be prompted for the password of the user account on your IoT device. Type it in carefully, as you won't see any characters appear on the screen as you type, which is normal for security reasons. Once the password is correct, you'll be logged into your device's command line, and you can start issuing commands as if you were sitting right in front of it. This is, basically, your first successful remote session.
While passwords are okay for initial setup, for better security and convenience, you'll want to switch to SSH keys. We'll talk more about SSH keys in the next section, but just know that they offer a much stronger way to authenticate your connection without needing to type a password every time. This is especially useful for automated tasks or for managing many devices, you know?
Beyond the Basics: Advanced SSH for IoT
Once you're comfortable with basic SSH connections, there are some clever ways to use SSH that can make your IoT projects even more efficient. These advanced SSH tricks for your IoT tutorial projects go beyond just logging in. They help you deal with more complex network setups and add even stronger layers of safety, which is really quite handy.
Whether you're a beginner or have some experience, this comprehensive tutorial aims to give you the knowledge and skills to securely access and manage your IoT devices. So, buckle up because this is where things get even more interesting, you know?
SSH Keys: A Stronger Lock
SSH keys provide a much more secure and convenient way to log into your IoT devices than passwords. An SSH key pair consists of two parts: a private key, which you keep secret on your computer, and a public key, which you place on your IoT device. When you try to connect, your computer uses the private key to prove its identity to the device, which then checks it against the public key. If they match, you're granted access without needing a password. This is a very robust way to handle access.
To set this up, you'll first generate an SSH key pair on your computer (using a command like `ssh-keygen`). Then, you'll copy the public key to your IoT device, typically into a file named `authorized_keys` within the `.ssh` directory of your user's home folder. This process removes the need for passwords, making your connections both safer and quicker. It's a fundamental step for serious IoT management, honestly.
SSH Tunneling: Reaching Devices Behind Routers
So, you're curious about remote SSH IoT behind a router? Well, this is where the magic happens for real. Many IoT devices are located behind firewalls or routers that prevent direct incoming connections from the internet. This is a common security measure, but it makes remote access tricky. SSH tunneling, also known as port forwarding, lets you create a secure channel through an intermediate server to reach your device. It's like building a secret, protected passageway through a wall, in a way.
There are different types of SSH tunnels: local, remote, and dynamic. For reaching an IoT device behind a router, a reverse SSH tunnel (a type of remote port forwarding) is often used. This involves the IoT device initiating an outgoing connection to a publicly accessible server, and then that server acts as a relay for your incoming SSH connection. This method is incredibly useful for managing devices that don't have a public IP address or are on a private network, which is a fairly common situation.
Secure Tunneling with AWS IoT
For those using cloud platforms, services like AWS IoT Secure Tunneling offer a managed way to establish these connections. An AWS IoT secure tunneling tutorial shows how to open a tunnel and start an SSH session without needing to manage your own intermediate server. This service helps companies safely allow IoT remote SSH access for their IoT devices, which is a big advantage for large-scale deployments.
This approach simplifies the setup of secure remote access, especially for devices that are difficult to reach directly. It handles the complexities of network traversal and authentication, providing a reliable and secure path to your devices. It's a very streamlined way to achieve remote control, you know?
Port Forwarding for IoT
While SSH tunneling often refers to creating a secure channel for a single service, "port forwarding" can also describe configuring your router to direct specific incoming traffic to a device on your local network. For example, you might set up your router to forward incoming SSH requests (on port 22) to your IoT device's local IP address. This method requires a public IP address for your network and careful configuration of your router's settings, which can be a bit more exposed than tunneling.
It's important to be cautious with port forwarding, as it can expose your device directly to the internet. If you use this method, you must ensure your IoT device's SSH server is extremely secure, using SSH keys and disabling password login. It's a simpler setup, perhaps, but it comes with increased security considerations, so be careful.
Keeping Your IoT SSH Connections Safe
Securing your SSH connections for IoT devices is just as important as setting them up. Without proper security practices, even the most robust SSH setup can be vulnerable. This section covers good habits to keep your connections safe, making sure your IoT devices remain protected from potential threats. These tips will help you safeguard your IoT and keep it safe from harm, truly.
This comprehensive tutorial aims to walk you through the fundamentals of creating a firewall for IoT devices using SSH. We will look into understanding IoT security risks, setting up a firewall, configuring SSH for secure access, and putting in place good habits for ongoing security. It's about building a strong defense, you know?
Strong Passwords and Key Management
If you're still using passwords for SSH, make sure they are very strong. This means long, complex passwords that combine uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols. Even better, as mentioned, switch to SSH key-based authentication. Once you're using keys, disable password login on your IoT device's SSH server. This is a major security upgrade, as private keys are much harder to guess or crack than passwords, obviously.
Managing your SSH keys is also crucial. Keep your private keys secure on your computer, perhaps protected with a strong passphrase. Never share your private keys with anyone. Regularly review the public keys on your IoT devices to ensure
- How Much Are The Raiders Worth
- Who Is The Nfl Owner And Girlfriend Pregnant
- Who Is Kristin Fishers Husband
- Whats Brian Kilmeades Salary On Fox News
- How Many Years Are Raiders In Vegas
SSH Tutorial: What is SSH, Encryptions and Ports

What Is SSH? | How to Use SSH (Secure Shell) | Gcore

What is a Secure Shell Protocol (SSH)? Everything to Know